This article is about the history of the Indian subcontinent prior to the partition of India in 1947. For the the modern Republic of India, see History of the Republic of India. For Pakistan and Bangladesh, see History of Pakistan and History of Bangladesh. For South India, see History of South India.
| Part of a series on the |
| History of India |
|---|
 |
| Chronology of Indian history |
| Ancient India |
|---|
Prehistoric India and Vedic India
Religions, Society, Mahajanapadas
|
Mauryan Period
Economy, Spread of Buddhism,
Chanakya, Satavahana Empire
|
The Golden Age
Discoveries, Aryabhata,
Ramayana, Mahabharata
|
| Medieval India |
|---|
The Classical Age
Art, Philosophy, Literature
|
Islam in India
Delhi Sultanate, Vijayanagara Empire,
Music, Guru Nanak
|
Mughal India
Architecture,
Maratha Confederacy
|
| Modern India |
|---|
Company Rule
Zamindari system, Warren Hastings,
Mangal Pandey, 1857
|
British Indian Empire
Hindu reforms, Bengal Renaissance,
Independence struggle, Mahatma Gandhi
|
The history of India begins with evidence of human activity of Homo sapiens as long as 75,000 years ago hominids (Homo Erectus) from about 500,000 years ago. The Indus Valley Civilization, which spread and flourished in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent from c. 3300 to 1300 BCE, was the first major civilization in India. A sophisticated and technologically advanced urban culture developed in the Mature Harappan period, from 2600 to 1900 BCE. This Bronze Age civilization collapsed at the beginning of the second millennium BCE and was followed by the Iron Age Vedic Civilization, which extended over much of the Indo-Gangetic plains and which witnessed the rise of major polities known as the Mahajanapadas. In one kingdom, Magadha, Mahavira and Gautama Buddha were born in the 6th or 5th century BCE, who propagated their Shramanic philosophies.
Almost all of the subcontinent was conquered by the Maurya Empire during the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE. It subsequently became fragmented, with various parts ruled by numerous Middle kingdoms for the next 1,500 years. This is known as the classical period of India, during which India is estimated to have had the largest economy of the ancient and medieval world, controlling between one third and one fourth of the world's wealth up to the 18th century.
Much of Northern and Central India was once again united in the 4th century CE, and remained so for two centuries thereafter, under the Gupta Empire. This period, of Hindu religious and intellectual resurgence, is known among its admirers as the "Golden Age of India." During the same time, and for several centuries afterwards, Southern India, under the rule of the Chalukyas, Cholas, Pallavas and Pandyas, experienced its own golden age. During this period aspects of Indian civilization, administration, culture, and religion (Hinduism and Buddhism) spread to much of Asia.
The southern state of Kerala had maritime business links with the Roman Empire from around 77 CE. Islam was introduced in Kerala through this route by Muslim traders. Muslim rule in the subcontinent began in 712 CE when the Arab general Muhammad bin Qasim conquered Sindh and Multan in southern Punjab, setting the stage for several successive invasions between the 10th and 15th centuries CE from Central Asia, leading to the formation of Muslim empires in the Indian subcontinent such as the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire.
Mughal rule came to cover most of the northern parts of the subcontinent. Mughal rulers introduced middle-eastern art and architecture to India. In addition to the Mughals and various Rajput kingdoms, several independent Hindu states, such as the Vijayanagara Empire, the Maratha Empire and the Ahom Kingdom, flourished contemporaneously in Southern, Western and North-Eastern India respectively. The Mughal Empire suffered a gradual decline in the early eighteenth century, which provided opportunities for the Afghans, Balochis, Sikhs and the Marathas to exercise control over large areas in the northwest of the subcontinent until the British East India Company gained ascendancy over South Asia.
Beginning in the mid-18th century and over the next century, India was gradually annexed by the British East India Company. Dissatisfaction with Company rule led to the First War of Indian Independence, after which India was directly administered by the British Crown and witnessed a period of both rapid development of infrastructure and economic decline. During the first half of the 20th century, a nationwide struggle for independence was launched by the Indian National Congress, and later joined by the Muslim League. The subcontinent gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1947, after being partitioned into the dominions of India and Pakistan.
Contents- 1 Pre-Historic era
- 1.1 Stone Age
- 1.2 Bronze Age
- 1.3 Vedic period
- 1.4 Maha Janapadas
- 1.5 Persian and Greek conquests
- 2 Maurya period
- 3 Early Middle Kingdoms — The Golden Age
- 3.1 Northwestern hybrid cultures
- 3.2 Roman trade with India
- 3.3 Gupta rule
- 4 Late Middle Kingdoms — The Classical Age
- 5 The Islamic Sultanates
- 6 The Mughal era
- 7 Post-Mughal period
- 8 Colonial era
- 9 The Indian Independence movement
- 10 Independence and Partition
- 11 See also
- 12 References
- 13 Further reading
- 14 External links
|
Pre-Historic era
Stone Age
Main article: South Asian Stone Age
Further information: Mehrgarh, Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka, and Edakkal Caves
 Bhimbetka rock painting, Madhya Pradesh, India. |  Alleged Stone age writings of Edakkal Caves in Kerala, India. |
Isolated remains of Homo erectus in Hathnora in the Narmada Valley in Central India indicate that India might have been inhabited since at least the Middle Pleistocene era, somewhere between 200,000 to 500,000 years ago. Recent finds in Tamil Nadu (at c. 75,000 years ago, before and after the explosion of the Toba volcano) indicate the presence of the first anatomically modern humans in the area.
The Mesolithic period in the Indian subcontinent was followed by the Neolithic period, when more extensive settlement of the subcontinent occurred after the end of the last Ice Age, or approximately 12,000 years ago. The first confirmed semi-permanent settlements appeared 9,000 years ago in the Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka in modern Madhya Pradesh, India.
Early Neolithic culture in South Asia is represented by the Mehrgarh findings (7000 BCE onwards) in present day Balochistan, Pakistan. Traces of a Neolithic culture have been alleged to be submerged in the Gulf of Khambat in India, radiocarbon dated to 7500 BCE. However, the one dredged piece of wood in question was found in an area of strong ocean currents. Neolithic agriculture cultures sprang up in the Indus Valley region around 5000 BCE, in the Lower Gangetic valley around 3000 BCE, and in later South India, spreading southwards and also northwards into Malwa around 1800 BCE.
Tools crafted by proto-humans have been discovered in the north-western part of the subcontinent that have been dated back two million years. The ancient history of the region includes some of South Asia's oldest settlements and some of its major civilizations.
The earliest archaeological site in the Subcontinent is the palaeolithic hominid site in the Soan River valley.
Village life is first attested at the Neolithic site of Mehrgarh, while the first urban civilization of the region began with the Indus Valley Civilization.
Bronze Age
Main article: Indus Valley Civilization

Ancient Lothal as envisaged by the Archaeological Survey of India. 
"Priest King" of Indus Valley Civilization The Bronze Age in the Indian subcontinent began around 3300 BCE with the early Indus Valley Civilization. It was centered on the Indus River and its tributaries which extended into the Ghaggar-Hakra River valley, the Ganges-Yamuna Doab, Gujarat, and southeastern Afghanistan.
The civilization is primarily located in modern day India (Gujarat, Haryana, Punjab and Rajasthan provinces) and Pakistan (Sindh, Punjab, and Balochistan provinces). Historically part of Ancient India, it is one of the world's earliest urban civilizations, along with Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt. Inhabitants of the ancient Indus river valley, the Harappans, developed new techniques in metallurgy and handicraft (carneol products, seal carving) produced copper, bronze, lead and tin.
The Mature Indus civilization flourished from about 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE marked the beginning of the urban civilization on the subcontinent. The ancient civilization included urban centers such as Dholavira, Kalibangan, Rupar, Rakhigarhi, Lothal in modern day India and Harappa, Ganeriwala, Mohenjo-daro in modern day Pakistan. The civilization is noted for its cities built of brick, road-side drainage system and multi-storied houses.
Vedic period
Main article: Vedic Civilization
See also: Vedas and Indo-Aryans
Map of North India in the late Vedic period. The Vedic period is characterized by Indo-Aryan culture associated with the texts of Vedas, sacred to Hindus, which were orally composed in Vedic Sanskrit. The Vedas are some of the oldest extant texts, next to those of Egypt and Mesopotamia. The Vedic period lasted from about 1500 BCE to 500 BCE, laid the foundations of Hinduism and other cultural aspects of early Indian society. The Aryas established Vedic civilization all over North India, and increasingly so in the Gangetic Plain. This period succeeded the prehistoric Late Harappan during which immigrations of Indo-Aryan speaking tribes overlaid the existing civilizations of local people whom they called Dasyus.
Early Vedic society consisted of largely pastoral groups, with late Harappan urbanization having been abandoned. After the Rigveda, Aryan society became increasingly agricultural, and was socially organized around the four Varnas. In addition to the principal texts of Hinduism the Vedas, the core themes of the Sanskrit epics Ramayana and Mahabharata are said to have their ultimate o
The swastika is a major Hindu iconography. rigins during this period. Early Indo-Aryan presence probably corresponds, in part, to the presence of Ochre Coloured Pottery in archaeological findings.
The kingdom of the Kurus corresponds to the Black and Red Ware and Painted Gray Ware culture and the beginning of the Iron Age in Northwestern India, around 1000 BCE with the composition of the Atharvaveda, the first Indian text to mention iron, as śyāma ayas, literally "black metal." The Painted Grey Ware culture spanning much of Northern India was prevalent from about 1100 to 600 BCE. The Vedic Period also established republics (such as Vaishali) which existed as early as the sixth century BCE and persisted in some areas until the fourth century CE. The later part of this period corresponds with an increasing movement away from the prevalent tribal system towards establishment of kingdoms, called Maha Janapadas.
Maha Janapadas

Gautama Buddha undertaking extreme ascetic practices before his enlightenment on the bank of river Falgu in Bodh Gaya, Bihar. 
Detail of a leaf with, The Birth of Mahavira (the 24th Jain Tirthankara), from the Kalpa Sutra, c.1375-1400.
The Mahajanapadas were the sixteen most powerful kingdoms and republics of the era, located mainly across the fertile Indo-Gangetic plains, however there were a number of smaller kingdoms stretching the length and breadth of Ancient India. 
Nalanda University is considered "one of the first great universities in recorded history." It was the center of Buddhist learning and research in the world from 450–1193 CE.
Main articles: Mahajanapadas and Magadha Empire
Main articles: History of Hinduism, History of Buddhism, and History of Jainism
See also: Adi Shankara, Siddhartha Gautama, and Mahavira
Further information: Upanishads, Indian Religions, Indian philosophy, and Ancient universities of India
In the later Vedic Age, a number of small kingdoms or city states had covered the subcontinent, many mentioned during Vedic, early Buddhist and Jaina literature as far back as 1000 BCE. By 500 BCE, sixteen monarchies and 'republics' known as the Mahajanapadas — Kasi, Kosala, Anga, Magadha, Vajji (or Vriji), Malla, Chedi, Vatsa (or Vamsa), Kuru, Panchala, Machcha (or Matsya), Surasena, Assaka, Avanti, Gandhara, Kamboja — stretched across the Indo-Gangetic plains from modern-day Afghanistan to Bengal and Maharastra. This period was that of the second major urbanisation in India after the Indus Valley Civilization.
Many smaller clans mentioned within early literature seem to have been present across the rest of the subcontinent. Some of these kings were hereditary; other states elected their rulers. The educated speech at that time was Sanskrit, while the dialects of the general population of northern India are referred to as Prakrits. Many of the sixteen kingdoms had coalesced to four major ones by 500/400 BCE, by the time of Siddhartha Gautama. These four were Vatsa, Avanti, Kosala and Magadha.
Hindu rituals at that time were complicated and conducted by the priestly class. It is thought that the Upanishads, late Vedic texts dealing mainly with incipient philosophy, were composed in the later Vedic Age and early in this period of the Mahajanapadas (from about 600 - 400 BCE). Upanishads had a substantial effect on Indian philosophy, and were contemporary to the development of Buddhism and Jainism, indicating a golden age of thought in this period.
It is believed that in 537 BCE, that Siddhartha Gautama attained the state of "enlightenment", and became known as the 'Buddha' - the enlightened one. Around the same time, Mahavira (the 24th Jain Tirthankara according to Jains) propagated a similar theology, that was to later become Jainism. However, Jain orthodoxy believes it predates all known time. The Vedas are believed to have documented a few Jain Tirthankars, and an ascetic order similar to the sramana movement.
The Buddha's teachings and Jainism had doctrines inclined toward asceticism, and were preached in Prakrit, which helped them gain acceptance amongst the masses. They have profoundly influenced practices that Hinduism and Indian spiritual orders are associated with namely, vegetarianism, prohibition of animal slaughter and ahinsa (non-violence). While the geographic impact of Jainism was limited to India, Buddhist nuns and monks eventually spread the teachings of Buddha to Central Asia, East Asia, Tibet, Sri Lanka and South East Asia.
Persian and Greek conquests
See also: Achaemenid Empire, Greco-Buddhism, Alexander the Great, Nanda Empire, and Gangaridai
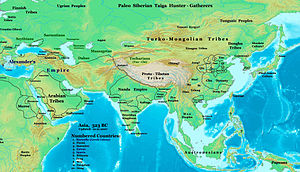
Asia in 323 BCE, the Nanda Empire and Gangaridai Empire in relation to Alexander's Empire and neighbors.
Much of the northwestern subcontinent (present day Eastern Afghanistan and Pakistan) came under the rule of the Persian Achaemenid Empire in c. 520 BCE during the reign of Darius the Great, and remained so for two centuries thereafter. In 326 BCE, Alexander the Great conquered Asia Minor and the Achaemenid Empire, reaching the north-west frontiers of the Indian subcontinent. There, he defeated King Puru in the Battle of the Hydaspes (near modern-day Jhelum, Pakistan) and conquered much of the Punjab. Alexander's march East put him in confrontation with the Nanda Empire of Magadha and Gangaridai Empire of Bengal. His army, exhausted and frightened by the prospect of facing larger Indian armies at the Ganges River, mutinied at the Hyphasis (modern Beas) and refused to march further East. Alexander, after the meeting with his officer, Coenus, was convinced that it was better to return.
The Persian and Greek invasions had important repercussions on Indian civilization. The political systems of the Persians was to influence future forms of governance on the subcontinent, including the administration of the Mauryan dynasty. In addition, the region of Gandhara, or present-day eastern Afghanistan and north-west Pakistan, became a melting pot of Indian, Persian, Central Asian and Greek cultures and gave rise to a hybrid culture, Greco-Buddhism, which lasted until the 5th century CE and influenced the artistic development of Mahayana Buddhism.
Maurya period
Main article: Maurya Empire
Further information: Chandragupta Maurya, Bindusara, and Ashoka the Great
 Maurya Empire under Ashoka the Great |  Ashokan pillar at Vaishali, 3rd century BCE. |
The Maurya Empire (322–185 B.C), ruled by the Mauryan dynasty, was geographically extensive, powerful, and a political military empire in ancient India. The great Maurya empire was established by Chandragupta Maurya and this empire was flourished by Ashoka the Great. At its greatest extent, the Empire stretched to the north along the natural boundaries of the Himalayas, and to the east stretching into what is now Assam. To the west, it reached beyond modern Pakistan, annexing Balochistan and much of what is now Afghanistan, including the modern Herat and Kandahar provinces. The Empire was expanded into India's central and southern regions by the emperors Chandragupta and Bindusara, but it excluded a big portion of unexplored tribal and forested regions near Kalinga which was won by Ashoka the Great. Ashoka propagated Buddhism across the world and established many Buddhist monuments.
Chandragupta's minister Chanakya wrote the Arthashastra, one of the greatest treatises on economics, politics, foreign affairs, administration, military arts, war, and religion produced in Asia. Archaeologically, the period of Mauryan rule in South Asia falls into the era of Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW). The Arthashastra and the Edicts of Ashoka are primary sources of written records of the Mauryan times. The Lion Capital of Asoka at Sarnath, is the national emblem of India.
Early Middle Kingdoms — The Golden Age
Main article: Middle Kingdoms of India
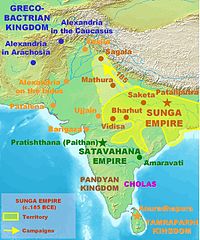
Ancient India during the rise of Sunga Empire and Satavahana Empire. | |  Kushan Empire and Western Satraps of Ancient India in the north along with Pandyans and Early Cholas in southern India. |
The middle period was a time of notable cultural development. The Satavahanas, also known as the Andhras, was a dynasty which ruled in southern and central India starting from around 230 BC. Satakarni, the sixth ruler of the Satvahana dynasty, defeated the Sunga Empire of North India. Afterwards, Kharavela the warrior king of Kalinga ruled a vast empire and was responsible for the propagation of Jainism in the Indian Subcontinent. The Kharavelan Jain empire also had a formidable maritime empire with trading routes linking it to Sri Lanka, Burma, Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia, Borneo, Bali, Sumatra and Java. Colonists from Kalinga settled in Sri Lanka, Burma, as well as the Maldives and Malay Archipelago. Kuninda Kingdom was a small Himalayan state that survived from around the 2nd century BC to roughly the 3rd century CE. The Kushanas migrated into north-western India in the middle of the 1st century CE, from Central Asia, and founded an empire that eventually stretched from Tajikistan to the middle Ganges. The Western Satraps (35-405 CE) were Saka rulers of the western and central part of India. They were the successors of the Indo-Scythians (see below) and contemporaneous with the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, and the Satavahana (Andhra) who ruled in central and southern India.
Different empires such as the Pandyans, Cholas, Cheras, Kadambas, Western Gangas, Pallavas and Chalukyas dominated the southern part of the Indian peninsula, at different periods of time. Several southern kingdoms formed overseas empires that stretched across South East Asia. The kingdoms warred with each other and Deccan states, for domination of the south. Kalabhras, a Buddhist kingdom, briefly interrupted the usual domination of the Cholas, Cheras and Pandyas in the South.
Northwestern hybrid cultures

The founder of the Indo-Greek Kingdom, Demetrius I "the Invincible" (205–171 BCE). See also: Indo-Greek kingdom, Indo-Scythians, Indo-Parthian Kingdom, and Indo-Sassanids
The north-western hybrid cultures of the subcontinent included the Indo-Greeks, the Indo-Scythians, the Indo-Parthians, and the Indo-Sassinids. The first of these, the Indo-Greek Kingdom, founded when the Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius invaded the region in 180 BC, extended over various parts of present-day Afghanistan and Pakistan. Lasting for almost two centuries, it was ruled by a succession of more than 30 Greek kings, who were often in conflict with each other. The Indo-Scythians was a branch of the Indo-European Sakas (Scythians), who migrated from southern Siberia first into Bactria, subsequently into Sogdiana, Kashmir, Arachosia, Gandhara and finally into India; their kingdom lasted from the middle of the 2nd century BC to the 1st century BC. Yet another kingdom, the Indo-Parthians (also known as Pahlavas) came to control most of present-day Afghanistan and northern Pakistan, after fighting many local rulers such as the Kushan ruler Kujula Kadphises, in the Gandhara region. The Sassanid empire of Persia, who were contemporaries of the Guptas, expanded into the region of present-day Pakistan, where the mingling of Indian and Persian cultures gave birth to the Indo-Sassanid culture.
Roman trade with India
Main article: Roman trade with India

Coin of the Roman emperor Augustus found at the Pudukottai, South India. Roman trade with India started around 1 CE following the reign of Augustus and his conquest of Egypt, theretofore India's biggest trade partner in the West.
The trade started by Eudoxus of Cyzicus in 130 BCE kept increasing, and according to Strabo (II.5.12.), by the time of Augustus up to 120 ships were setting sail every year from Myos Hormos to India. So much gold was used for this trade, and apparently recycled by the Kushans for their own coinage, that Pliny (NH VI.101) complained about the drain of specie to India:
"India, China and the Arabian peninsula take one hundred million sesterces from our empire per annum at a conservative estimate: that is what our luxuries and women cost us. For what percentage of these imports is intended for sacrifices to the gods or the spirits of the dead?"
—Pliny, Historia Naturae 12.41.84.
These trade routes and harbour are described in detail in the 1st century CE Periplus of the Erythraean Sea.
Gupta rule
Main article: Gupta Empire
See also: Chandra Gupta I, Samudragupta, Chandra Gupta II, Kumaragupta I, and Skandagupta
Further information: Kalidasa, Aryabhatta, Varahamihira, Vishnu Sharma, and Vatsyayana
Further information: Meghadūta, Abhijñānaśākuntala, Kumārasambhava, Panchatantra, Aryabhatiya, Indian numerals, and Kama Sutra
|  Kalidasa's Sanskrit play Abhijñānaśākuntala is one of the Legacy of the Gupta Empire. |
The Classical Age refers to the period when much of the Indian Subcontinent was reunited under the Gupta Empire (ca. 320 AD–550 AD). This period is called the Golden Age of India and was marked by extensive achievements in science, technology, engineering, art, dialectic, literature, logic, mathematics, astronomy, religion and philosophy that crystallized the elements of what is generally known as Hindu culture. The decimal numeral system, including the concept of zero, was invented in India during this period. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the pursuit of scientific and artistic endeavors in India.
The high points of this cultural creativity are magnificent architectures, sculptures and paintings. The Gupta period produced scholars such as Kalidasa, Aryabhatta, Varahamihira, Vishnu Sharma, and Vatsyayana who made great advancements in many academic fields. Science and political administration reached new heights during the Gupta era. Strong trade ties also made the region an important cultural center and set the region up as a base that would influence nearby kingdoms and regions in Burma, Sri Lanka, Malay Archipelago and Indochina.
The Gupta period marked a watershed of Indian culture: the Guptas performed Vedic sacrifices to legitimize their rule, but they also patronized Buddhism, which continued to provide an alternative to Brahmanical orthodoxy. The military exploits of the first three rulers—Chandragupta I (ca. 319–335), Samudragupta (ca. 335–376), and Chandragupta II (ca. 376–415) —brought much of India under their leadership. They successfully resisted the North-Western Kingdoms until the arrival of the Hunas who established themselves in Afghanistan by the first half of the fifth century, with their capital at Bamiyan. Nevertheless, much of the Deccan and southern India were largely unaffected by this state of flux in the north.
Late Middle Kingdoms — The Classical Age
Main article: Middle Kingdoms of India
 | |  |
Pala Empire under Dharmapala | | Pala Empire under Devapala |
Chola Empire under Rajendra Chola c. 1030 C.E. The Kanauj Triangle was the focal point of empires - the Rashtrakutas of Deccan, the Gurjara Pratiharas of Malwa, and the Palas of Bengal.
The Classical Age in India began with the Guptas and the resurgence of the north during Harsha's conquests around the 7th century, and ended with the fall of the Vijayanagar Empire in the South, due to pressure from the invaders to the north in the 13th century. This period produced some of India's finest art, considered the epitome of classical development, and the development of the main spiritual and philosophical systems which continued to be in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. King Harsha of Kannauj succeeded in reuniting northern India during his reign in the 7th century, after the collapse of the Gupta dynasty. His kingdom collapsed after his death.
From the 7th to the 9th century, three dynasties contested for control of northern India: the Gurjara Pratiharas of Malwa, the Palas of Bengal and the Rashtrakutas of Deccan. The Sena Empire would later assume control of the Pala Empire, and the Gurjara Pratiharas fragmented into various states. These were the first of the Rajputs, a series of kingdoms which managed to survive in some form for almost a millennium until Indian independence from the British. The first recorded Rajput kingdoms emerged in Rajasthan in the 6th century, and small Rajput dynasties later ruled much of northern India. One Gurjar Rajput of the Chauhan clan, Prithvi Raj Chauhan, was known for bloody conflicts against the advancing Islamic Sultanates. The Shahi dynasty ruled portions of eastern Afghanistan, northern Pakistan, and Kashmir from the mid-seventh century to the early eleventh century.
The Chalukya Empire ruled parts of southern and central India from 550 to 750 from Badami, Karnataka and again from 970 to 1190 from Kalyani, Karnataka. The Pallavas of Kanchi were their contemporaries further to the south. With the decline of the Chalukya empire, their feudatories, Hoysalas of Halebidu, Kakatiya of Warangal, Seuna Yadavas of Devagiri and a southern branch of the Kalachuri divided the vast Chalukya empire amongst themselves around the middle of 12th century.
The Chola Empire at its peak covered much of the Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Rajaraja Chola conquered all of peninsular South India and parts of the Sri Lanka. Rajendra Chola's navies went even further, occupying coasts from Burma (now Myanmar) to Vietnam, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Sumatra, and the Malaya in South East Asia and Pegu islands. Later during the middle period, the Pandyan Empire emerged in Tamil Nadu, as well as the Chera Empire in Kerala. By 1343, all these dynasties had ceased to exist giving rise to the Vijayanagar empire.
The ports of South India were involved in the Indian Ocean trade, chiefly involving spices, with the Roman Empire to the west and Southeast Asia to the east. Literature in local vernaculars and spectacular architecture flourished till about the beginning of the 14th century when southern expeditions of the sultan of Delhi took their toll on these kingdoms. The Hindu Vijayanagar dynasty came into conflict with Islamic rule (the Bahmani Kingdom) and the clashing of the two systems, caused a mingling of the indigenous and foreign culture that left lasting cultural influences on each other. The Vijaynagar Empire eventually declined due to pressure from the first Delhi Sultanates who had managed to establish themselves in the north, centered around the city of Delhi by that time.
The Islamic Sultanates
Main article: Islamic Empires in India
See also: Bahmani Sultanate and Deccan Sultanates
After conquering Per

Gol Gumbaz at Bijapur, has the second largest pre-modern dome in the world after the Byzantine Hagia Sophia. sia, Islamic Caliphate incorporated parts of what is now Pakistan around 720 CE. They were keen to invade India, which was the richest classical civilization, with a flourishing international trade and the only known diamond mines in the world. After several wars over three centuries between various north Indian kingdoms and the Caliphate, short lived Islamic empires (Sultanates) were established and spread across the northern subcontinent over a period of a few centuries. But, prior to Turkic invasions, Muslim trading communities had flourished throughout coastal South India, particularly in Kerala, where they arrived in small numbers, mainly from the Arabian peninsula, through trade links via the Indian Ocean. However, this had marked the introduction of an Abrahamic Middle Eastern religion in Southern India's pre-existing Indian religions, often in puritanical form. Later, the Bahmani Sultanate and Deccan Sultanates flourished in the south.
Delhi Sultanate
Main article:
Delhi Sultanate 
Qutub Minar is the world's tallest brick minaret, commenced by Qutb-ud-din Aybak of the Slave dynasty. In the 12th and 13th centuries, Turkics and Pashtuns invaded parts of northern India and established the Delhi Sultanate at the beginning of the 13th century, in the former Rajput holdings. The subsequent Slave dynasty of Delhi managed to conquer large areas of northern India, approximate to the ancient extent of the Guptas, while the Khilji Empire was also able to conquer most of central India, but were ultimately unsuccessful in conquering and uniting most of the subcontinent. The Sultanate ushered in a period of Indian cultural renaissance. The resulting "Indo-Muslim" fusion of cultures left lasting syncretic monuments in architecture, music, literature, religion, and clothing. It is surmised that the language of Urdu (literally meaning "horde" or "camp" in various Turkic dialects) was born during the Delhi Sultanate period as a result of the inter-mingling of the local speakers of Sanskritic Prakrits with the Persian, Turkic and Arabic speaking immigrants under the Muslim rulers. The Delhi Sultanate is the only Indo-Islamic empire to stake a claim to enthroning one of the few female rulers in India, Razia Sultan (1236–1240).
A Turco-Mongol conqueror Timur began a trek starting in 1398 to invade the reigning Sultan Nasir-u Din Mehmud of the Tughlaq Dynasty in the north Indian city of Delhi. The Sultan's army was defeated on December 17, 1398. Timur entered Delhi and the city was sacked, destroyed and left in ruins; his army fell killing and plundering for three days and nights. He ordered except for the Sayyids, the scholars, and the other Mussulmans, the whole city to be sacked; 100,000 war prisoners, mostly Hindus, were put to death in one day.
The Mughal era
 Extent of the Mughal Empire in 1700. |  Taj Mahal, built by the Mughals |
Main article: Mughal Empire
See also: Babur, Humayun, Akbar the Great, Jahangir, Shah Jahan, and Aurangzeb
In 1526, Babur, a Timurid descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan, swept across the Khyber Pass and established the Mughal Empire. However, his son Humayun was defeated by the Afghan warrior Sher Shah Suri in the year 1540, and Humayun was forced to retreat to Kabul. After Sher Shah's death his son Islam Shah and Hindu king Samrat Hem Chandra Vikramaditya, who had won 22 battles from Punjab to Bengal and had established a secular Hindu Raj, ruled North India from Delhi till 1556, when Akbar's forces defeated and killed Hemu in the Second Battle of Panipat on 6th Nov. 1556. The Mughal Dynasty ruled most of the Indian subcontinent by 1600; it went into a slow decline after 1707 and was finally defeated during the 1857 War of Independence also called the Indian Rebellion of 1857. This period marked vast social change in the subcontinent as the Hindu majority were ruled over by the Mughal emperors; most of them showed religious tolerance, liberally patronising Hindu culture. The famous emperor Akbar, who was the grandson of Babar, tried to establish a good relationship with the Hindus. However, later emperors such as Aurangazeb tried to establish complete Muslim dominance and as a result several historical temples were destroyed during this period and taxes imposed on non-Muslims. During the decline of the Mughal Empire, which at its peak occupied an area similar to the ancient Maurya Empire, several smaller empires rose to fill the power vacuum or themselves were contributing factors to the decline. The Mughals were perhaps the richest single dynasty to have ever existed. In 1739, Nader Shah defeated the Mughal army at the huge Battle of Karnal. After this victory, Nader captured and sacked Delhi, carrying away many treasures, including the Peacock Throne. During the Mughal era, the dominant political forces consisted of the Mughal Empire and its tributaries and, later on, the rising successor states - including the Maratha confederacy - who fought an increasingly weak and disfavoured Mughal dynasty. The Mughals, while often employing brutal tactics to subjugate their empire, had a policy of integration with Indian culture, which is what made them successful where the short-lived Sultanates of Delhi had failed. Akbar the Great was particularly famed for this. Akbar declared "Amari" or non-killing of animals in the holy days of Jainism. He rolled back the Jazia Tax for non-Muslims. The Mughal Emperors married local royalty, allied themselves with local Maharajas, and attempted to fuse their Turko-Persian culture with ancient Indian styles, creating unique Indo-Saracenic architecture. It was the erosion of this tradition coupled with increased brutality and centralization that played a large part in their downfall after Aurangzeb, who unlike previous emperors, imposed relatively non-pluralistic policies on the general population, that often inflamed the majority Hindu population.
Post-Mughal period
Main articles: Maratha Empire, Kingdom of Mysore, Hyderabad State, Sikh Empire, Rajputs, and Durrani Empire
See also: History of Sikhism
Further information: Shivaji, Tippu Sultan, Nizam, Ranjit Singh, and Ahmad Shah Abdali
 The Maratha Empire in 1760. The last Hindu empire of India. |  Harmandir Sahib or The Golden Temple is culturally the most significant place of worship for the Sikhs. |
The post-Mughal era was dominated by the rise of the Maratha suzerainty as other small regional states (mostly post-Mughal tributary states) emerged, and also by the increasing activities of European powers (see colonial era below). The Maratha Kingdom was founded and consolidated by Shivaji. By the 18th century, it had transformed itself into the Maratha Empire under the rule of the Peshwas. By 1760, the Empire had stretched across practically the entire subcontinent. This expansion was brought to an end by the defeat of the Marathas by an Afghan army led by Ahmad Shah Abdali at the Third Battle of Panipat (1761). The last Peshwa, Baji Rao II, was defeated by the British in the Third Anglo-Maratha War.
Mysore was a kingdom of southern India, which was founded around 1400 CE by the Wodeyar dynasty. The rule of the Wodeyars was interrupted by Hyder Ali and his son Tippu Sultan. Under their rule Mysore fought a series of wars sometimes against the combined forces of the British and Marathas, but mostly against the British with some aid or promise of aid from the French. Hyderabad was founded by the Qutb Shahi dynasty of Golconda in 1591. Following a brief Mughal rule, Asif Jah, a Mughal official, seized control of Hyderabad declaring himself Nizam-al-Mulk of Hyderabad in 1724. It was ruled by a hereditary Nizam from 1724 until 1948. Both Mysore and Hyderabad became princely states in British India.
The Punjabi kingdom, ruled by members of the Sikh religion, was a political entity that governed the region of modern day Punjab. This was among the last areas of the subcontinent to be conquered by the British. The Anglo-Sikh wars marked the downfall of the Sikh Empire. Around the 18th century modern Nepal was formed by Gorkha rulers.
Colonial era
Main article: Colonial India
Vasco da Gama's maritime success to discover for Europeans a new sea route to India in 1498 paved the way for direct Indo-European commerce. The Portuguese soon set up trading-posts in Goa, Daman, Diu and Bombay. The next to arrive were the Dutch, the British—who set up a trading-post in the west-coast port of Surat in 1619—and the French. The internal conflicts among Indian Kingdoms gave opportunities to the European traders to gradually establish political influence and appropriate lands. Although these continental European powers were to control various coastal regions of southern and eastern India during the ensuing century, they would eventually lose all their territories in India to the British islanders, with the exception of the French outposts of Pondicherry and Chandernagore, the Dutch port of Travancore, and the Portuguese colonies of Goa, Daman, and Diu.
The British Raj
Main article: British Raj
The British East India Company had been given permission by the Mughal emperor Jahangir in 1617 to trade in India. Gradually their increasing influence led the de-jure Mughal emperor Farrukh Siyar to grant them dastaks or permits for duty free trade in Bengal in 1717. The Nawab of Bengal Siraj Ud Daulah, the de facto ruler of the Bengal province, opposed British attempts to use these permits. This led to the Battle of Plassey in 1757, in which the 'army' of East India Company, led by Robert Clive, defeated the Nawab's forces. This was the first political foothold with territorial implications that the British acquired in India. Clive was appointed by the Company as its first 'Governor of Bengal' in 1757. This was combined with British victories over the French at Madras, Wandiwash and Pondicherry that, along with wider British successes during the Seven Years War, reduced French influence in India. After the Battle of Buxar in 1764, the Company acquired the civil rights of administration in Bengal from the Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II; it marked the beginning of its formal rule, which was to engulf eventually most of India and extinguish the Moghul rule and dynasty itself in a century. The East India Company monopolized the trade of Bengal. They introduced a land taxation system called the Permanent Settlement which introduced a feudal-like structure (See Zamindar) in Bengal. By the 1850s, the East India Company controlled most of the Indian sub-continent, which included present-day Pakistan and Bangladesh. Their policy was sometimes summed up as Divide and Rule, taking advantage of the enmity festering between various princely states and social and religious groups.
The first major movement against the British Company's high handed rule resulted in the Indian Rebellion of 1857, also known as the "Indian Mutiny" or "Sepoy Mutiny" or the "First War of Independence". After a year of turmoil, and reinforcement of the East India Company's troops with British soldiers, the Company overcame the rebellion. The nominal leader of the uprising, the last Mughal emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar, was exiled to Burma, his children were beheaded and the Moghul line abolished. In the aftermath all power was transferred from the East India Company to the British Crown, which began to administer most of India as a colony; the Company's lands were controlled directly and the rest through the rulers of what it called the Princely states. There were 565 princely states when the Indian subcontinent gained independence from Britain in August 1947.
During the British Raj, famines in India, often attributed to failed government policies, were some of the worst ever recorded, including the Great Famine of 1876–78, in which 6.1 million to 10.3 million people died and the Indian famine of 1899–1900, in which 1.25 to 10 million people died. The Third Plague Pandemic started in China in the middle of the 19th century, spreading plague to all inhabited continents and killing 10 million people in India alone. Despite persistent diseases and famines, however, the population of the Indian subcontinent, which stood at about 125 million in 1750, had reached 389 million by 1941.
The Indian Independence movement
Main articles: Indian independence movement and Pakistan Movement
See also: Mahatma Gandhi and Freedom fighters of India

Rabindranath Tagore is Asia's first Nobel laureate and composer of national anthems of both India and Bangladesh. 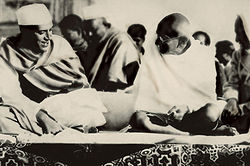
Gandhi and Nehru in 1937.The physical presence of the British in India was not significant. Yet the British were able to rule two-thirds of the subcontinent directly, and exercise considerable leverage over the Princely States that accounted for the remaining one-third. The British employed "Divide and Rule" in British India as a means of preventing an uprising against the Raj.
In this environment of Hindu-Muslim disunity, the first step toward Indian independence and western-style democracy was taken with the appointment of Indian councilors to advise the British viceroy, and with the establishment of provincial Councils with Indian members; the councillors' participation was subsequently widened in legislative councils. From 1920 leaders such as Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi began highly popular mass movements to campaign against the British Raj, using largely peaceful methods. Some other revolutionaries adopted militant approach; revolutionary activities against the British rule took place throughout the Indian sub-continent. The profound impact Gandhi had on India and his ability to gain independence through a totally non-violent mass movement made him lead by example, wearing a minimum of homespun clothes to weaken the British textile industry and orchestrating a march to the sea, where demonstrators proceeded to make their own salt in protest against the British monopoly. Indians gave him the name Mahatma, or Great Soul, first suggested by the Bengali poet Rabindranath Tagore. Subash Chandra Bose, a great freedom fighter, had organised a formidable army to fight against the British rule. Bhagat Singh was another Indian freedom fighter, considered to be one of the most influential revolutionaries of the Indian independence movement; he is often referred to as Shaheed Bhagat Singh (the word shaheed means "martyr"). These movements succeeded in bringing Independence to the Indian sub-continent in 1947. One year later, Gandhi was assassinated. However, he did live long enough to free his homeland and is thus recognised as the father of his nation.
Independence and Partition
Main articles: Partition of India, History of the Republic of India, History of Pakistan, and History of Bangladesh
Along with the desire for independence, tensions between Hindus and Muslims had also been developing over the years. The Muslims had always been a minority, and the prospect of an exclusively Hindu government made them wary of independence; they were as inclined to mistrust Hindu rule as they were to resist the foreign Raj, although Gandhi called for unity between the two groups in an astonishing display of leadership. The British, extremely weakened by the World War II, promised that they would leave and the British Indian territories gained independence in 1947, after being partitioned into the Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan. Following the controversial division of pre-partition Punjab and Bengal, rioting broke out between Sikhs, Hindus and Muslims in these provinces and spread to several other parts of India, leaving some 500,000 dead. Also, this period saw one of the largest mass migrations ever recorded in modern history, with a total of 12 million Hindus, Sikhs and Muslims moving between the newly created nations of India and Pakistan (which gained independence on 15 and 14 August 1947 respectively). In 1971, Bangladesh, formerly East Pakistan and East Bengal, seceded from Pakistan. The histories of each of these modern nations can be found on the respective pages shown above.
Source:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_India















 The Indian subcontinent consists of a number of separate linguistic communities each of which share a common language and culture. The people of India speak many languages and dialects which are mostly varieties of about 15 principal languages.
The Indian subcontinent consists of a number of separate linguistic communities each of which share a common language and culture. The people of India speak many languages and dialects which are mostly varieties of about 15 principal languages.  ndia has been known to have wonderful dresses and costumes. Indian dressing styles are marked by many variations, both regional and religious. One is likely to witness a plethora of colors, texture and styles in Indian clothing. To a foreigner, the powerful attraction is the colorful attire of the people in India. With globalization, dresses are also getting westernized. Though the majority of the first generation Indian women wear traditional costumes, the newer generation are more experimental and wear Indian, Indo-western and Western suits. The majority of men are more comfortable in western clothing. Men from all classes and regions of India wear shirts and trousers
ndia has been known to have wonderful dresses and costumes. Indian dressing styles are marked by many variations, both regional and religious. One is likely to witness a plethora of colors, texture and styles in Indian clothing. To a foreigner, the powerful attraction is the colorful attire of the people in India. With globalization, dresses are also getting westernized. Though the majority of the first generation Indian women wear traditional costumes, the newer generation are more experimental and wear Indian, Indo-western and Western suits. The majority of men are more comfortable in western clothing. Men from all classes and regions of India wear shirts and trousers 












 Location: On the banks of river Yamuna in Agra
Location: On the banks of river Yamuna in Agra


























